Hey there, sun-seekers! We all love soaking up the sun, but there’s a downside – sunburn and sun poisoning. Knowing the difference is key to enjoying the sun without the ouch.
Today, we’re breaking down how to prevent, treat, and deal with the duration of these sun troubles. So, grab your shades and let’s dive into the sunny side of things!
What’s the difference between sunburn and sun poisoning?
Sunburn and sun poisoning are two distinct reactions that occur when the skin is exposed to excessive sunlight. While both conditions result from prolonged exposure to the sun’s harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays, they differ in terms of severity and symptoms.
Sunburn
Sunburn is the milder of the two conditions and is a common consequence of spending too much time in the sun without proper protection. When the skin is exposed to UV rays, it triggers the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin colour. However, excessive UV exposure can overwhelm the skin’s defences, leading to sunburn.
The symptoms of sunburn include redness, pain, and sometimes swelling of the affected areas. Sunburn typically occurs a few hours after sun exposure and can last for several days. In more severe cases, blistering may occur.
To prevent sunburn, it is crucial to use sunscreen with a high SPF, wear protective clothing, and seek shade during peak sunlight hours.
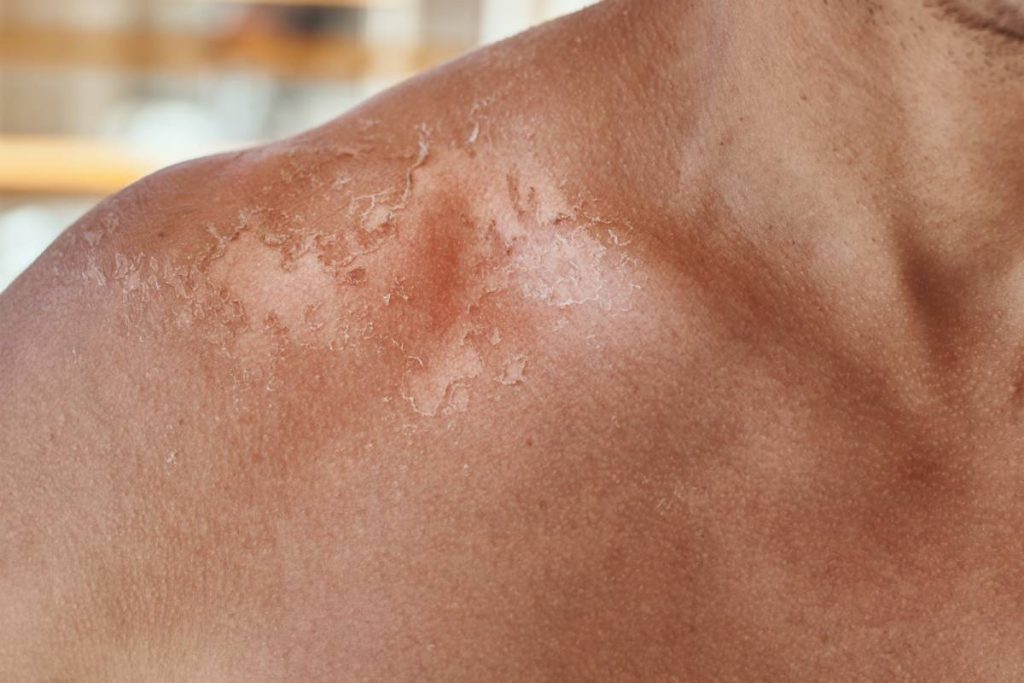
Sun Poisoning
Sun poisoning, on the other hand, is a more severe reaction to sun exposure and is often considered an extreme form of sunburn. It is characterized by a set of symptoms that go beyond the typical sunburn signs.
Symptoms of sun poisoning include severe redness, blistering, swelling, nausea, vomiting, headache, dizziness, and fever. Unlike sunburn, sun poisoning may require medical attention, especially if there are systemic symptoms like nausea and fever.
One major difference is that sun poisoning affects not only the outer layer of the skin but can also involve deeper layers. This can result in a more intense and prolonged healing process compared to regular sunburn.
How long does sunburn and sun poisoning last?
Sunburn and sun poisoning are uncomfortable consequences of overexposure to the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays. The duration of these conditions can vary based on factors such as severity, individual skin characteristics, and the promptness of treatment.
Sunburn
Sunburn is typically a temporary condition that can last anywhere from a few days to a couple of weeks, depending on its severity. Mild sunburn, characterized by redness and slight discomfort, may resolve within a few days with proper care.
Moderate sunburn, which involves more significant redness, swelling, and possibly blistering, may take up to a week or two to heal. It’s crucial to consistently follow recommended at-home treatments during this period, such as applying aloe vera gel, cool compresses, and staying well-hydrated.
Severe sunburn, marked by widespread blistering and intense pain, may take longer to heal, potentially extending beyond two weeks. In such cases, seeking medical advice is advisable to manage pain and prevent complications.

Sun Poisoning
Sun poisoning is a more severe form of sunburn, often associated with systemic symptoms. The duration of sun poisoning can be longer than that of typical sunburn, and it may require medical intervention.
Mild cases of sun poisoning may share a timeline similar to moderate sunburn, resolving within one to two weeks with appropriate care. However, due to the additional symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and fever, recovery may be more complex.
In more severe instances of sun poisoning, where medical attention is necessary, the duration of symptoms can vary. Intravenous (IV) fluids and prescribed medications can expedite the healing process, but full recovery may still take several weeks.
Factors Influencing Duration
- Severity of Exposure: The intensity and duration of sun exposure directly impact the severity of sunburn or sun poisoning. Prolonged exposure without adequate protection increases the likelihood of more extensive damage and a longer recovery period.
- Skin Type: Individuals with fair or sensitive skin may experience more prolonged symptoms compared to those with darker skin tones. Lighter skin tends to burn more quickly and severely.
- Promptness of Treatment: Early and consistent treatment significantly influences recovery time. Taking immediate action with cooling measures, hydrating the skin, and using over-the-counter remedies can expedite the healing process.
- Individual Healing Response: Each person’s body reacts differently to sun damage. Factors such as overall health, immune system function, and genetics play a role in the speed of recovery.
Tips for Faster Recovery
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated, helping the body heal from the inside out.
- Moisturize: Apply gentle, fragrance-free moisturizers to keep the skin hydrated and promote healing.
- Avoid Sun Exposure: During the healing process, it’s crucial to protect the affected areas from further sun exposure. Wear protective clothing and use sunscreen even on cloudy days.
- Rest: Allow your body to recover by getting adequate rest, especially if systemic symptoms are present.
- Medical Consultation: If symptoms are severe or persistent, seek medical advice for appropriate treatment and management.
What’s the prevention and treatment for sunburn and sun poisoning?
Prevention
Preventing sunburn and sun poisoning involves adopting sun-safe practices to shield your skin from the sun’s powerful rays. Here are some straightforward and effective preventive measures:
- Sunscreen: Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a Sun Protection Factor (SPF) of at least 30. Apply it generously to all exposed skin, even on cloudy days. Reapply every two hours, or more frequently if swimming or sweating.
- Protective Clothing: Wear protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts, pants, beach towels and wide-brimmed hats, to minimize direct sun exposure. Light and loose-fitting clothing can provide additional comfort.
- Seek Shade: Limit your time in direct sunlight, especially during peak hours from 10 a.m. to 4 p.m. If possible, seek shade under trees, umbrellas, or other structures.
- Sunglasses: Protect your eyes from UV rays by wearing sunglasses that block both UVA and UVB rays. Look for sunglasses labelled as providing 100% UV protection.
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration helps maintain the skin’s resilience. Drink plenty of water, especially when spending extended periods in the sun.

Treatment for Sunburn
In the unfortunate event of sunburn, there are several simple and soothing measures you can take at home to alleviate discomfort:
- Cool Compresses: Apply cool compresses or take cool baths to help reduce skin temperature and soothe the burn. Avoid using very cold water, as it may worsen the situation.
- Aloe Vera Gel: Aloe vera has natural anti-inflammatory properties. Applying aloe vera gel can help cool the skin and promote healing.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to prevent dehydration, which is common with sunburn. Staying hydrated supports the body’s healing process.
- Over-the-counter Creams: Use over-the-counter creams containing hydrocortisone to reduce inflammation and redness. Follow the instructions on the product carefully.
- Pain Relievers: Non-prescription pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. Always follow recommended dosages.
Treatment for Sun Poisoning
Sun poisoning requires a higher level of attention due to its more severe symptoms. If you suspect sun poisoning, consider the following:
- Medical Attention: Seek medical help if you experience severe symptoms like nausea, vomiting, headache, dizziness, or fever. A healthcare professional can provide appropriate guidance and treatment.
- Hydration: Sun poisoning can lead to dehydration. Ensure you drink plenty of fluids, and in severe cases, intravenous (IV) fluids may be necessary under medical supervision.
- Cooling Measures: Apply cool compresses, take cool baths, or use cold packs to relieve discomfort. Avoid ice directly on the skin.
- Prescription Medications: In severe cases, a healthcare provider may prescribe corticosteroids or other medications to address inflammation and systemic symptoms.
- Rest and Recovery: Allow your body time to recover by resting and avoiding further sun exposure. This includes staying indoors or in shaded areas until symptoms improve.
Conclusion
Alright, sun enthusiasts, let’s wrap it up. Sunburn and sun poisoning may try to rain on our sunny parade, but fear not! With sunscreen, cool tricks for sunburn, and a nod to medical help for sun poisoning, we’ve got this. The sun is our friend, and armed with these tips, we can bask in its glow without the burn. Cheers to sunny days and healthy, happy skin!










